
- Boron is essential for all plant growth. It is important for cell wall structure, root growth, and pollination.
- Corn requires an adequate supply of available boron, especially during tasseling and silking. Where needed, a preplant application of Granubor® or a foliar spray of Solubor® prior to these stages of growth generally will ensure an adequate supply of boron to prevent and correct boron deficiency in corn.
- Only certain varieties of field corn under high-yield conditions—and some sweet corn varieties—may respond to applied boron, especially on sandy soils in high rainfall regions, or with adverse weather conditions during the critical stages of tasseling and silking.
- In order to avoid toxicity, application rates of boron and methods should be followed.
High fertility soil is necessary to meet corn's nutrient requirements. Well-drained soils with a good supply of organic matter which have been well fertilized and limed over several years will generally produce the highest grain yields.
Cell wall strength, cell division, seed development and sugar transport are plant functions of boron. While boron requirements for optimum plant nutrition are low as compared with those of the macronutrients, the need for boron is especially significant during tasseling and silking stages.
Boron deficiency in corn: symptoms
The most common symptom of boron deficiency in corn is small, misshapen cobs with missing kernels, resulting in significantly decreased yields. Under cases of extreme boron deficiency, the leaves also may have small white dead spots, streaking, and be brittle.
Soil tests and plant analyses
Boron deficiencies may occur on coarse-textured soils where organic matter content is low, on soils with a pH above 7.0, and on recently limed soils.
Soil testing and plant analyses are both helpful in assessing the potential boron-supplying capacity of the soil and the current boron status of the growing plant.
The critical level of hot-water-soluble boron for corn in most soils ranges from 0.2 to 0.5 ppm, depending on the soil pH, organic matter content and texture. Corn grown on soils that are lower than the critical level may respond to applied boron, depending on the hybrid and the weather conditions during the critical stages of reproduction.
The critical level of boron in the upper mature corn leaves is about 5 ppm, but the usual leaf-boron range is 10-20 ppm. Corn plants with leaf boron contents below the critical level should be sprayed with Solubor before tasseling and silking.
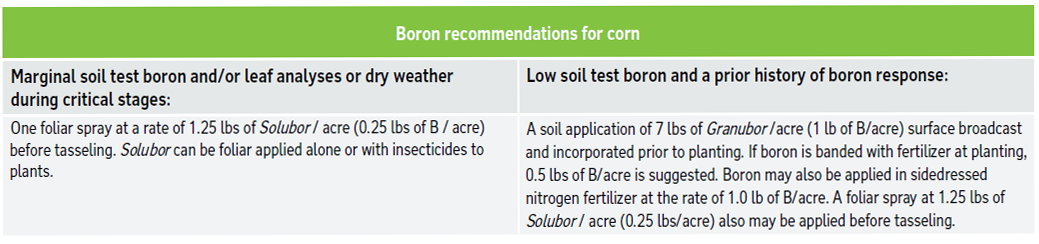
Corn fertilizer recommendations
Yield responses to applied boron may be inconsistent and seasonal, probably due to environmental effects on crop growth. However, boron fertilizer may improve sweet corn yield and high-yield field corn output, especially on sandy soils in high rainfall regions, or with over-irrigation because soluble boron can be easily leached from the root zone. Adverse weather conditions also can decrease the supply of available boron in soil and/or boron uptake by the plant during the critical stages of tasseling and silking. Response to applied boron generally is greatest when there are adequate supplies of other nutrients.
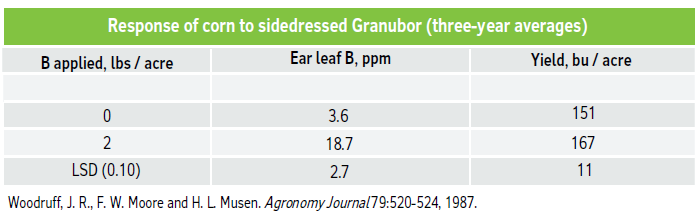
Data below show increased corn yields with a sidedressed application of boron with high potassium fertilization on a sandy soil. Other studies have reported corn yield increases with foliar sprays of 1.25 lbs of Solubor / acre prior to tasseling.
Download Agronomy Notes